Summary: SGLang: Efficient Execution of Structured Language Model Programs
Materials
1. What is the paper about?
Proposes SGLang, a Python-embedded DSL and efficiently execute multi-call, structured LLM workflows.
Key runtime ideas: RadixAttention for KV-cache reuse, compressed finite-state machine (cFSM) for fast constrained (e.g., JSON/regex) decoding, and API speculative execution for black-box endpoints.
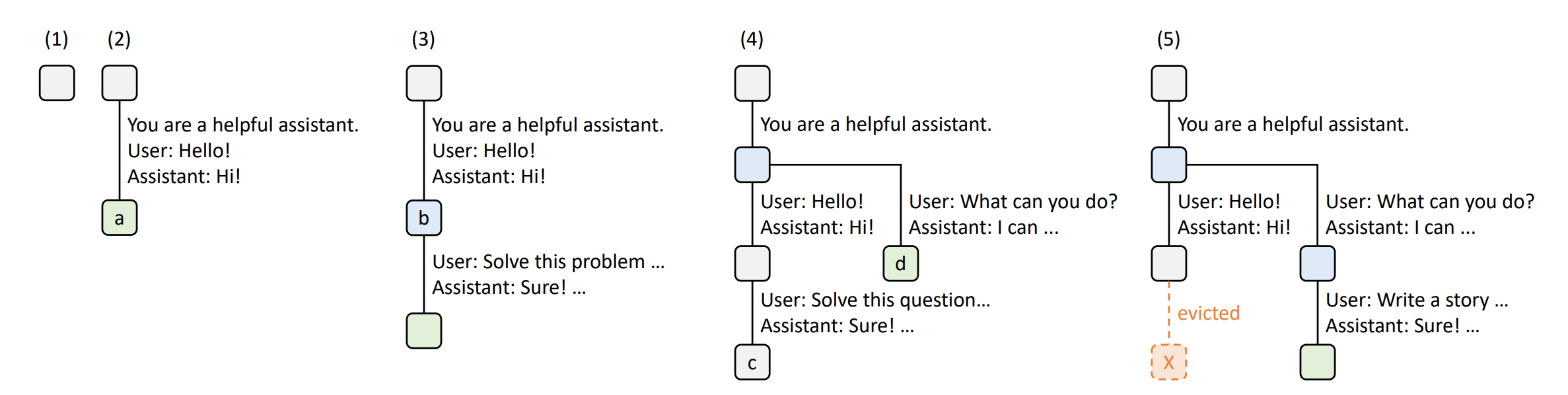
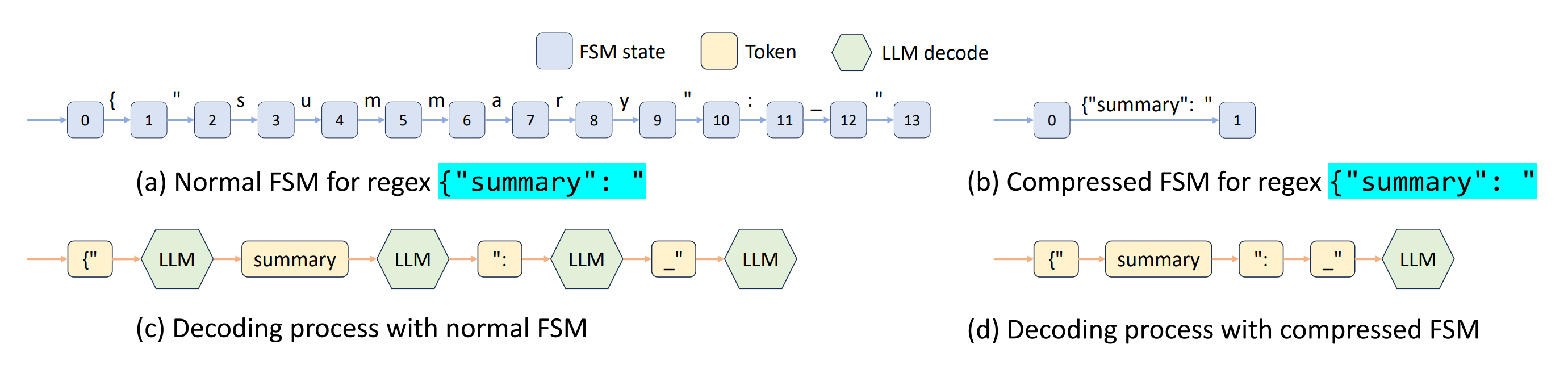
2. What is new about this specific paper, compared to prior work?
Treats the KV cache as a tree-based LRU cache (radix tree) with cache-aware scheduling and frontend/runtime co-design; authors argue this is the first solution supporting multi-level sharing, LRU eviction, co-scheduling, and distributed cases.
Prior engines (e.g., vLLM/PagedAttention) do memory paging and simple prefix reuse but not tree-structured, multi-level reuse with LRU and scheduling.
Other reuse lines (e.g., PromptCache, ChunkAttention) explore modular or prefix-aware reuse, but either risk accuracy drops or focus on kernel-level changes rather than an integrated cache+scheduler+language design.
Introduces a compressed FSM so multiple tokens along deterministic paths are decoded in one pass—speeding up constrained decoding beyond token-by-token masking in prior systems.
3. What experiments were run to support the arguments in this paper?
Up to 6.4× higher throughput and 3.7× lower latency across MMLU, HellaSwag, ReAct/Generative agents, Tree-/Skeleton-of-Thought, JSON decoding, multi-turn chat, and a DSPy RAG pipeline.
Similar gains on Mixtral-8×7B and Llama-70B.
Big throughput gains on LLaVA-v1.5-7B (image) and LLaVA-NeXT-34B (video); e.g., 0.18 → 1.15 image/s and 0.02 → 0.10 frame/s.
Ablations show that each component (tree cache, scheduling, frontend hints/parallelism) contributes; cFSM yields ~1.6× throughput in JSON decoding.
4. What are the shortcomings/limitations of this paper?
The paper only compares to an earlier vLLM version. Results may shift as baselines evolve.
For cFSM, the appendix flags potential probability distortion for some regex choices—an accuracy concern to study further.
5. What is a reasonable next step to build upon this paper?
Adapt RadixAttention across memory tiers (DRAM/disk), add fuzzy semantic matching, fix possible starvation in cache-aware scheduling, and strengthen the compiler for static planning.
Harden support for multimodal workflows and compare against newer KV-reuse baselines (e.g., updated vLLM, ChunkAttention) under identical settings.
Appendix
Radix tree: a space-optimized trie whose edges can store sequences (not just single symbols), enabling efficient prefix search and insertion.
Structured decoding: generation under hard constraints (e.g., regex/CFG) by masking invalid tokens
Fuzzy semantic matching — an informal term for matching by meaning rather than exact text (e.g., vector/embedding similarity) and tolerating surface mismatch, often used in RAG-style retrieval.